
Just as the brain and spinal cord make up a continuous, uninterrupted structure, the cranial and spinal cavities that house them are also continuous. In the posterior (dorsal) cavity, the cranial cavity houses the brain, and the spinal cavity (or vertebral cavity) encloses the spinal cord. The posterior (dorsal) and anterior (ventral) cavities are each subdivided into smaller cavities. Subdivisions of the Posterior (Dorsal) and Anterior (Ventral) Cavities Deep describes a position farther from the surface of the body.Superficial describes a position closer to the surface of the body.Distal describes a position in a limb that is farther from the point of attachment or the trunk of the body.The brachium is proximal to the antebrachium. Proximal describes a position in a limb that is nearer to the point of attachment or the trunk of the body.Medial describes the middle or direction toward the middle of the body.The thumb (pollex) is lateral to the digits. Lateral describes the side or direction toward the side of the body.Inferior (or caudal) describes a position below or lower than another part of the body proper near or toward the tail (in humans, the coccyx, or lowest part of the spinal column).Superior (or cranial) describes a position above or higher than another part of the body proper.The popliteus is posterior to the patella. Posterior (or dorsal) Describes the back or direction toward the back of the body.Anterior (or ventral) Describes the front or direction toward the front of the body.For example, in the disorder hypertension, the prefix “hyper-” means “high” or “over,” and the root word “tension” refers to pressure, so the word “hypertension” refers to abnormally high blood pressure.

The root of a term often refers to an organ, tissue, or condition, whereas the prefix or suffix often describes the root.

Because these languages are no longer used in everyday conversation, the meaning of their words does not change.Īnatomical terms are made up of roots, prefixes, and suffixes. Anatomical terms derive from ancient Greek and Latin words. For example, is a scar “above the wrist” located on the forearm two or three inches away from the hand? Or is it at the base of the hand? Is it on the palm-side or back-side? By using precise anatomical terminology, we eliminate ambiguity.
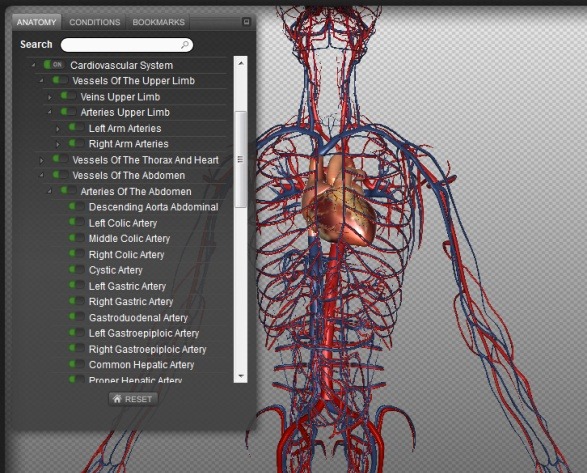
However, the purpose of this language is not to confuse, but rather to increase precision and reduce medical errors.

#Cu modern human anatomy program professional
The anatomy and physiology course was prepared on the basis of professional and the latest literature in accordance with the current curriculum at Polish Medical Universities, therefore it has been divided into sections using systemic anatomy supplemented with issues in physiology.Īnatomy and physiology are two complementary elements that allow you to perfectly understand the structure and functioning of the human body. The programme is dedicated to all high school graduates, pupils and students who want to supplement their knowledge in the field of anatomy and physiology that will be necessary during their studies. The Medical Poland Human Anatomy & Physiology Programme is designed by our experienced team based on many years of experience working with international medical students at Polish medical universities. The programme will help students prepare for challenging anatomy and physiology courses at the third level and will make those courses easier, as well as help, prepare for medical universities entrance exams.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
